
Home » Key Technologies Powering Financial Services Process Automation: RPA, AI, and Beyond

Financial institutions have continuously made efforts to deliver seamless banking experiences. However, with legacy systems, increasing compliance demands, and rising customer expectations, manual processes have become inefficient and unsustainable.
Today, automation is helping banks adapt to these pressures by transforming traditional operations into faster, smarter, and more modern systems. From large financial institutions to agile fintech startups, leaders are turning to automation to sustain growth and remain competitive.
However, financial services automation doesn’t work in isolation. Several key technologies are driving this shift. In this blog, we’ll explore the core technologies powering financial process automation—and how they’re making operations quicker, more accurate, and more responsive.
Automation is quickly growing among financial institutions all over the world. Technologies like RPA and AI are allowing banks to automate time-taking processes to optimize their completion from hours to minutes.
With its capabilities, Implementing financial services automation can enhance work efficiency, reduce costs, improve accuracy, and enable better decision-making. What started as a tool for reducing repetitive work is now turning into a key driver for transformation.
Here’s what market data says:
Get free Consultation and let us know your project idea to turn into an amazing digital product.
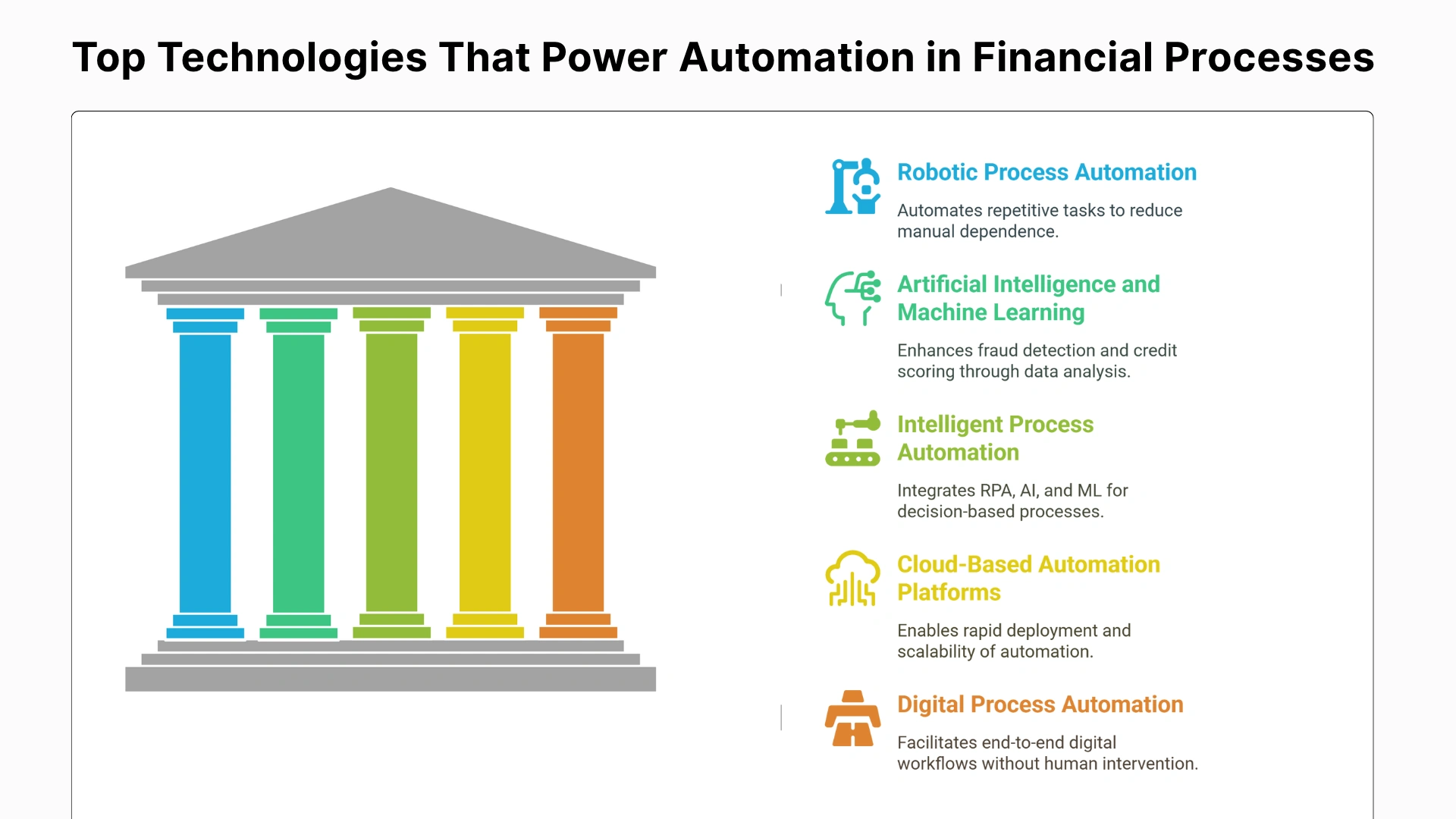
RPA is the most common automation platform and is used for automating tasks that are high in volume, follow repetitive procedures, or are rule-based. Banks of all sizes leverage this tool to complete workflows and reduce manual dependence.
AI analyses large datasets to uncover patterns and insights, while ML continuously improves performance based on past data. These technologies are used for fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and portfolio management.
IPA technology combines RPA, AI, ML, and advanced analytics into one cohesive automation layer. It helps banks in handling decision-based processes that often need human intervention, such as loan approvals or compliance checks.
Cloud platforms offer flexibility, scalability, and security for deploying automation tools across global operations. Banks using these platforms can adopt automation faster and integrate seamlessly with core banking systems.
DPA is a component of Hyperautomation which focuses on enabling end-to-end digital workflows in banks. Rather than automating the single process, it removes the need for human involvement and handles the whole process independently and accurately.
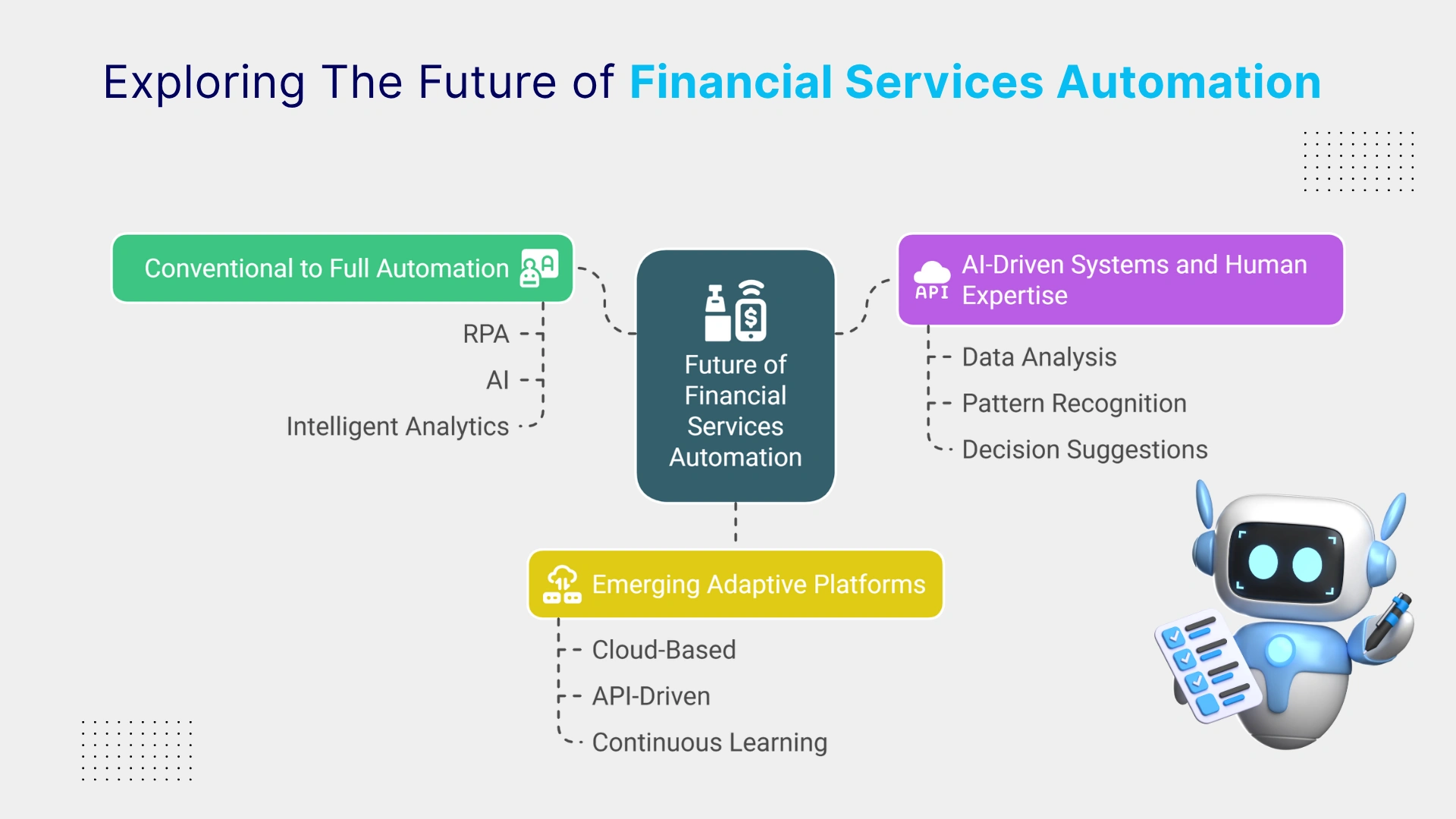
1. Conventional automation to full automation: The isolated implementation of automation might not be as common in the coming years. Banks may shift significantly toward full lifecycle integration, where automation combines RPA, AI, and intelligent analytics to enable end-to-end finance automation.
2. Combining AI-driven systems and human expertise: Rather than replacing humans, future automation systems will work alongside them. AI will handle large-scale data analysis, pattern recognition, and decision suggestions, while finance professionals focus on complex judgment calls, ethical considerations, and strategic planning.
3. Emerging adaptive platforms: Next-gen automation platforms will be built to adapt. These cloud-based, API-driven systems will continuously learn from data, adjust to regulatory shifts and scale with business needs.
Share your project idea with us. Together, we’ll transform your vision into an exceptional digital product!

Automation is great at improving workflows in banking. But what really makes it powerful are the tools and technologies that support it. Using RPA and AI helps financial institutions work faster, smarter, and with better accuracy.
Digital process automation further reduces manual work and allows staff to focus on improving customer service. As more banks use smart automation, it’s interesting to see how significantly artificial intelligence is transforming finance automation in 2025.
Yes, RPA systems maintain audit trails, never forget to log out, comply with governance frameworks, and follow strict security protocols. They’re often more secure than manual processes prone to human error.
Yes, cloud-based automation platforms make RPA and AI accessible to smaller institutions. These solutions offer scalable pricing models, reduced infrastructure costs, and faster deployment without requiring significant upfront investments.
RPA automates rule-based repetitive tasks, while AI analyzes large datasets, learns from patterns, and makes intelligent decisions. AI handles complex cognitive tasks like fraud detection, whereas RPA focuses on structured workflows.
Common challenges include legacy system integration, change management, staff training, initial investment costs, process standardization, and ensuring compliance with financial regulations while maintaining security and data integrity.
RPA doesn’t replace humans but augments their capabilities. It handles repetitive tasks while employees focus on customer service, strategic planning, complex decision-making, and relationship management that require human judgment and creativity.
RPA reduces operational costs by up to 70%, speeds up processes like KYC by 60%, minimizes human errors in data entry, and allows staff to focus on higher-value strategic activities.
Cloud platforms offer rapid deployment across multiple branches, scalable capacity during peak periods, reduced infrastructure costs, enhanced system uptime, and seamless integration with existing core banking systems.
The future involves end-to-end automation combining RPA, AI, and analytics, adaptive platforms that learn and adjust automatically, and human-AI collaboration where technology handles data analysis while humans focus on strategic decisions.
RPA shows up to 70% fewer manual errors compared to human processing. It consistently follows programmed rules, eliminates data entry mistakes, and maintains accuracy even during high-volume transaction periods.

Have a one on one discussion with our Expert Panel

Secure access is vital for organizations managing digital identities in today’s landscape. While both CIAM and IAM secure user identities, they serve different purposes — CIAM for customers and IAM for employees. This article explores their key differences and how to choose the right system.

For decades, traditional banking systems handled only basic transactions. The digital era exposed their limitations in speed and adaptability. Evolved core banking now powers seamless, future-ready financial services.

As digital expectations grow, customers now demand speed, ease of use, and 24/7 availability. To meet these demands at scale, digital-only banks choose business process automation in the banking industry to deliver consistent, responsive, and personalized service.

Founder and CEO

Chief Sales Officer
