
Home » From Legacy to Digital: The Core Banking Evolution Story

For several decades, banks operated using legacy core banking systems that were inflexible, batch-oriented, and costly to maintain. These traditional systems, while effective for basic deposits, withdrawals, and account management in their time, lacked the scalability and adaptability.
As digital transformation accelerated across industries, financial institutions began experiencing significant operational constraints with their existing infrastructure.
With the rise of digital banks and tech-driven challengers, the pressure to modernize banking operations became unavoidable. Core banking systems evolved from monolithic architectures into cloud-native, API-first ecosystems to operate and serve customers efficiently.
A core banking system is the central processing software of a bank. It manages customer accounts, deposits, loans, payments, and transaction posting across branches and digital channels. When integrated well, it lets customers access consistent services from any touchpoint: branch, web, or app.
Early core banking software ran on‑premises, was tightly coupled to proprietary hardware, and depended on legacy programming languages. These systems prioritized ledger integrity and internal control over customer experience. Change cycles were long, and most processing ran in end‑of‑day batches.
Limitations of Traditional Core Banking Technology include:
Did you know? Core banking system was first introduced in the late 1970s to shift from paper-based banking to computerized systems.
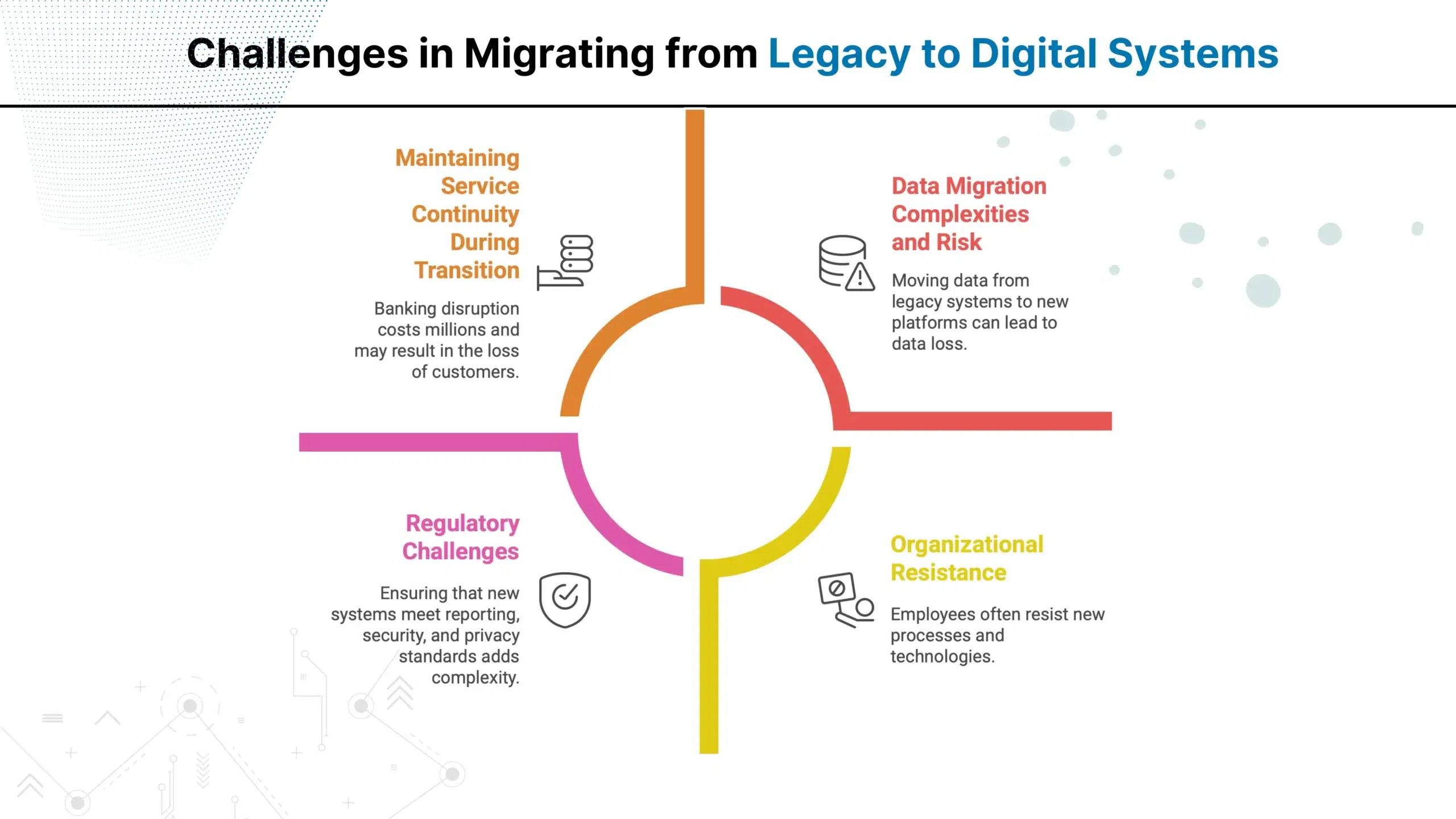
Legacy core banking systems were designed to meet the needs of the older era of banking. However, banking evolved, and demand increased for customer-first systems that provide instant services. Here are some main reasons for core banking transformation:
The rise of digital banks and mobile-first platforms introduced seamless and easily accessible services that legacy banking systems could not match. These new entrants offered instant transactions, intuitive interfaces, and zero branch dependency that met customer expectations.
To remain competitive, banks started adopting modern core banking solutions that support modern services.
Modern customers expect real-time transactions, 24/7 availability, and a personalized experience. Legacy systems, with their batch processing and downtime for updates, cannot deliver this level of availability.
This growing demand forced banks to shift toward digital banking systems that offer continuous uptime, scalable infrastructure, and personalized services to meet customer needs.
Global regulators enforced strict regulations around data security, transaction transparency, and reporting timelines. Legacy systems struggle with fragmented data structures, making it difficult to meet these evolving requirements.
Modern core banking transformation strategies integrate automation and other technologies to respond quickly to regulatory changes.
The maturity of cloud computing, API-driven ecosystems, and microservices has created an opportunity for banks to modernize their systems. Traditional cores, built as monolithic architectures, lack the flexibility to adopt new technologies.
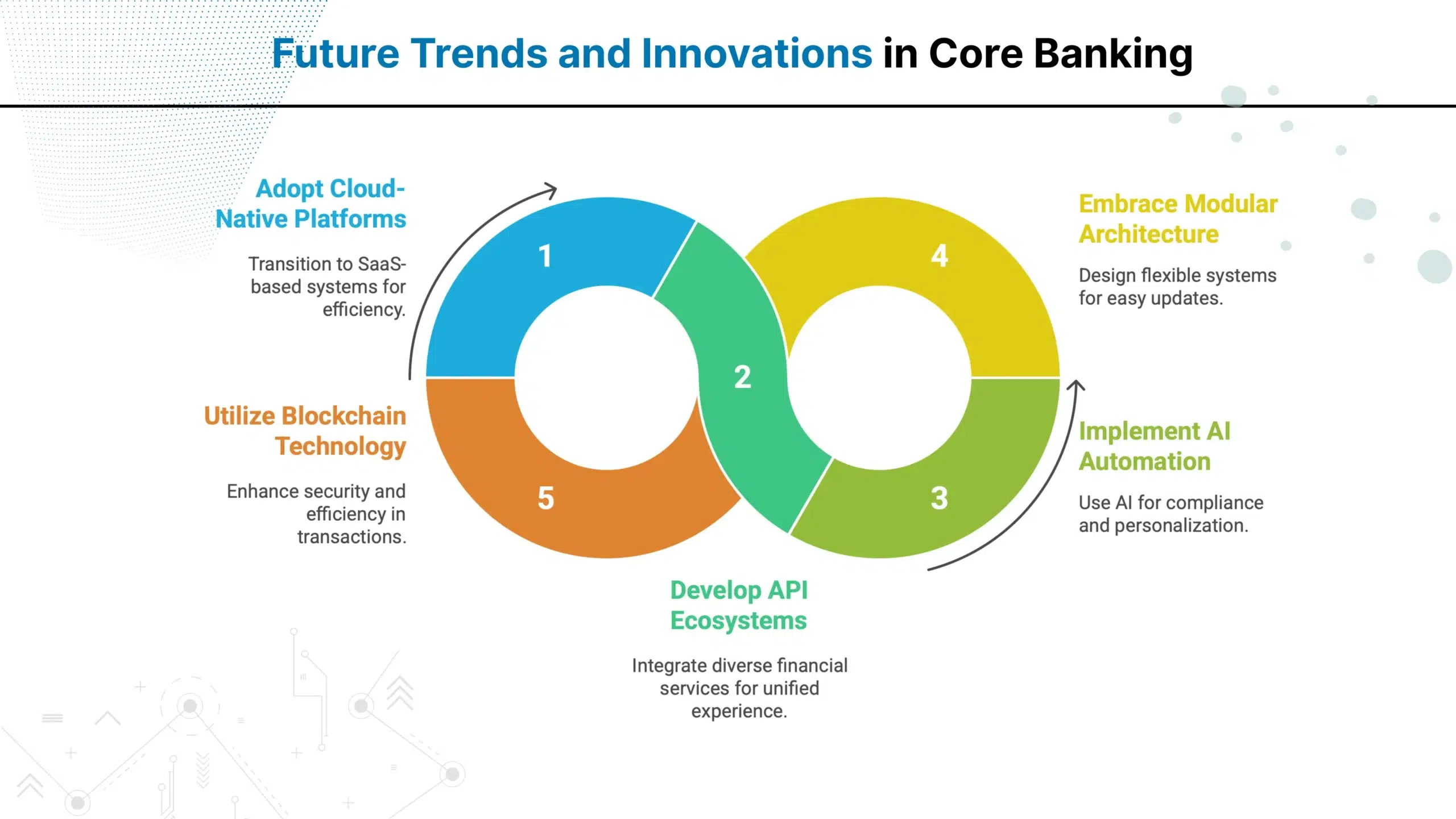
Banks now leverage core banking technology with modular designs, real-time processing, and cloud-native deployments to deliver faster, more scalable, and future-ready digital services.
Fintechs introduced agile, customer-centric services that banks can no longer afford to ignore. The rise of open banking and API-driven ecosystems forced banks to modernize their infrastructure to enable seamless third-party integrations.
Get free Consultation and let us know your project idea to turn into an amazing digital product.
Share your project idea with us. Together, we’ll transform your vision into an exceptional digital product!

A core banking system is centralized software that manages all banking operations, enabling real-time transactions and unified customer service across channels.
Traditional core banking uses batch processing and monolithic architecture, while digital systems offer real-time transactions, modular design, and cloud-native capabilities.
Modern platforms include real-time processing, API-first architecture, cloud deployment, microservices design, AI integration, and omnichannel customer experience capabilities.
Banks evaluate providers based on functionality, scalability, security, regulatory compliance, implementation timeline, total cost of ownership, and vendor reputation.
Cloud enables scalability, reduces infrastructure costs, improves disaster recovery, enables remote access, and supports rapid deployment of new banking services.
API-first design enables faster third-party integrations, supports fintech partnerships, accelerates product launches, and creates seamless omnichannel customer experiences.
AI improves fraud detection, automates compliance reporting, personalizes customer experiences, optimizes risk management, and enables predictive analytics for better decisions.
Digital transformation reduces operational costs, improves customer satisfaction, enables 24/7 services, accelerates product innovation, and enhances competitive positioning.
Open banking drives API standardization, enables third-party integrations, promotes innovation, increases competition, and requires modern core banking platform capabilities.
Success requires executive leadership, change management, staff training, vendor partnership, phased implementation, risk management, and continuous stakeholder communication.

Have a one on one discussion with our Expert Panel

In an era where technology shifts faster than any corporate strategy can keep up, the real concern for IT leaders is how their organization can leverage Microsoft effectively without disrupting operations. This is where the Microsoft Solutions Partner program becomes relevant.

Secure access is vital for organizations managing digital identities in today’s landscape. While both CIAM and IAM secure user identities, they serve different purposes — CIAM for customers and IAM for employees. This article explores their key differences and how to choose the right system.

As digital expectations grow, customers now demand speed, ease of use, and 24/7 availability. To meet these demands at scale, digital-only banks choose business process automation in the banking industry to deliver consistent, responsive, and personalized service.

Founder and CEO

Chief Sales Officer
