
Home » SQL vs NoSQL: Making the Right Decision for Your Use Case


Get free Consultation and let us know your project idea to turn into an amazing digital product.
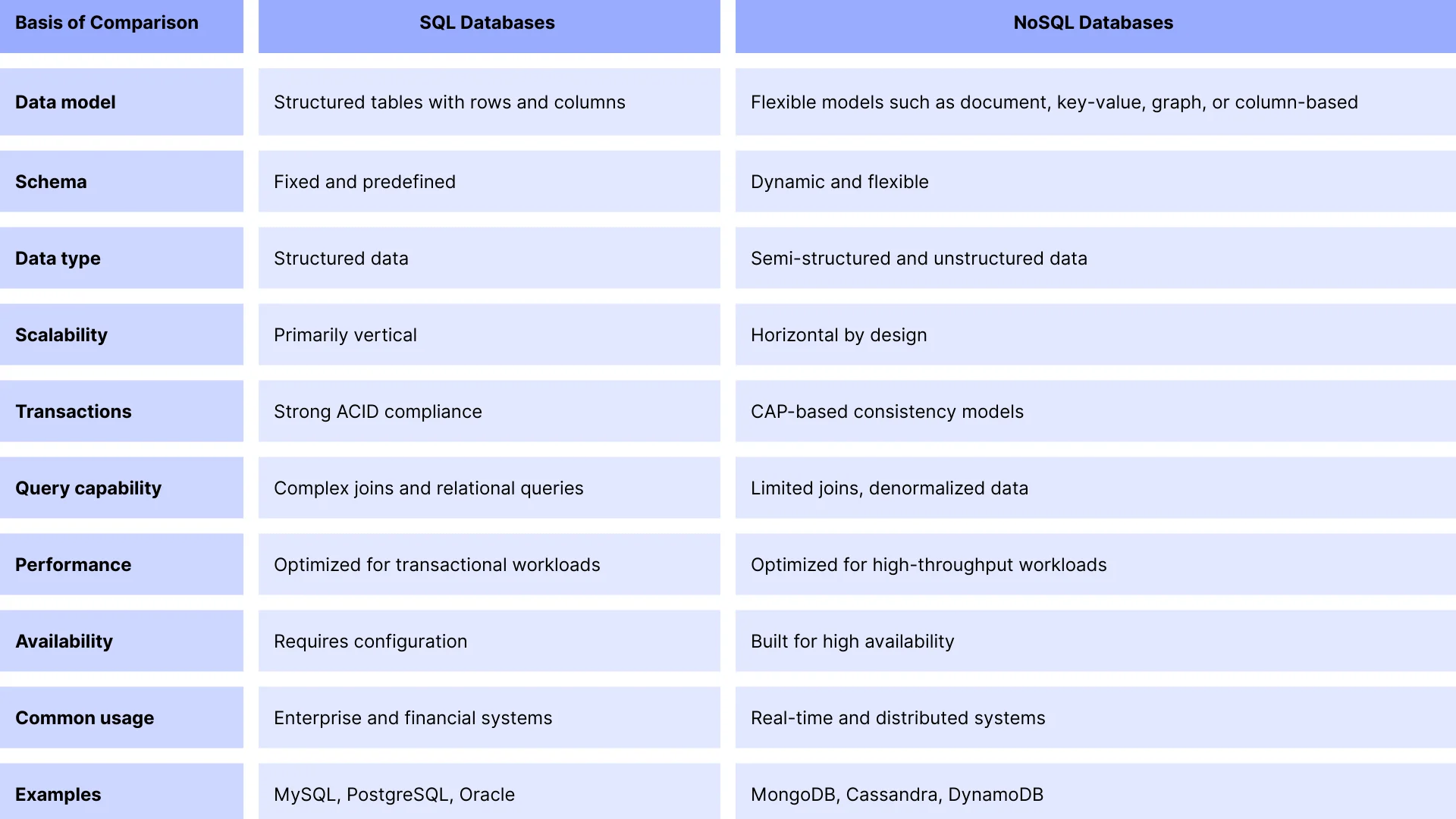
When evaluating sql vs nosql in real-world systems, performance, scalability, and security often carry more weight than data structure alone. These three factors directly influence user experience, system stability, and long-term growth.
Performance behavior differs significantly in the sql vs nosql comparison because each database is optimized for different workload patterns.
SQL databases perform exceptionally well in scenarios involving structured queries, complex joins, and transactional operations. Since data is normalized and relationships are clearly defined, SQL systems can execute precise queries efficiently, especially for reporting and analytical workloads.
However, as data volume increases and concurrency grows, performance can become constrained by the centralized nature of relational systems. Heavy write operations or large join queries may introduce latency if not carefully optimized.
In contrast, NoSQL databases are designed for high-throughput workloads. By storing data in denormalized formats and minimizing joins, NoSQL systems can deliver faster read and write operations at scale. This makes them highly effective for real-time applications, event-driven systems, and large user-facing platforms.
From a performance standpoint, sql vs nosql performance is less about speed alone and more about workload alignment. SQL excels in complex transactional queries, while NoSQL thrives in high-volume and low-latency environments.
Scalability is one of the most decisive factors in the sql vs nosql debate.
SQL databases traditionally scale vertically. This means improving performance by increasing server resources such as CPU, memory, or storage. While vertical scaling is straightforward, it has practical limits and often becomes expensive at large scale.
Some modern SQL systems support horizontal scaling, but it typically requires additional complexity and careful architectural planning.
NoSQL databases, by design, support horizontal scaling. Data is distributed across multiple nodes, allowing systems to scale simply by adding more servers. This approach improves fault tolerance and supports consistent performance even as traffic grows.
Because of this architecture, sql vs nosql scalability often favors NoSQL for applications that anticipate unpredictable growth, global user distribution, or massive concurrent workloads.
This scalability advantage is a major reason NoSQL databases are commonly used in microservices, cloud-native platforms, and large-scale consumer applications.
Security is a critical concern in any database decision, especially for regulated industries. In the sql vs nosql security discussion, both models offer strong protections, but their approaches differ.
SQL databases have a long history of enterprise-grade security features. These include role-based access control, strong authentication mechanisms, granular permissions, and mature auditing capabilities.
NoSQL databases have evolved significantly in recent years. Modern NoSQL platforms now support encryption at rest, encryption in transit, access control, and audit logging. However, security implementation often depends heavily on correct configuration and deployment practices.
From a governance perspective, SQL systems typically provide stricter enforcement by default, while NoSQL systems offer flexibility that must be managed carefully to avoid misconfigurations.
From an architectural standpoint, the sql vs nosql decision is rarely about choosing one over the other universally. Instead, it involves evaluating trade-offs:
In modern systems, it is increasingly common to use both approaches together. SQL may handle core transactional data, while NoSQL manages high-volume or real-time workloads. This hybrid strategy allows organizations to leverage the strengths of each model without forcing a one-size-fits-all solution.
Understanding performance behavior, scalability limits, and security implications provides the clarity needed to move forward confidently in the sql vs nosql databases selection process.
Evaluating the advantages and limitations of each database model is a critical step in the sql vs nosql decision-making process. Rather than treating one approach as superior, it is more effective to understand where each database excels and where it may introduce constraints.
SQL databases are widely valued for their strong emphasis on data consistency and accuracy. Their structured schema ensures that all stored data follows predefined rules, reducing the risk of invalid or inconsistent records. This reliability makes SQL databases especially suitable for transactional systems where correctness is essential.
Another major strength of SQL systems lies in their ability to support complex queries. Through joins and relational mapping, SQL databases can retrieve interconnected data efficiently, which is critical for reporting, analytics, and business intelligence use cases. Their mature ecosystem, backed by decades of development, also provides robust tools, documentation, and long-term stability.
Despite their strengths, SQL databases can face challenges in rapidly changing environments. Schema rigidity often makes frequent structural updates difficult and time-consuming, especially when applications evolve quickly.
Scalability can also become a concern in high-traffic systems. Traditional relational databases rely heavily on vertical scaling, which can increase costs and introduce performance bottlenecks under heavy load. These constraints often emerge during sql vs nosql evaluations for fast-growing applications.
NoSQL databases are built with flexibility and scale in mind. Their schema-less or schema-flexible design allows applications to adapt to changing data requirements without complex migrations. This capability supports faster development cycles and easier experimentation.
Another significant advantage is horizontal scalability. NoSQL databases can distribute data across multiple nodes, enabling systems to handle large volumes of traffic and data growth efficiently. This design aligns well with cloud-native architectures and distributed systems, making NoSQL a strong contender in many sql vs nosql databases comparisons.
While NoSQL databases offer flexibility, this same flexibility can introduce complexity if not managed properly. The absence of enforced relationships may require additional logic at the application level, increasing development responsibility.
Consistency behavior can vary depending on the database design, which may not suit applications that require strict transactional guarantees. Query capabilities are also less standardized, meaning developers must adapt to database-specific approaches. These factors become important when assessing the sql vs nosql difference beyond performance alone.
From an architectural standpoint, the sql vs nosql pros and cons discussion reinforces a key principle. SQL databases prioritize structure, reliability, and control, while NoSQL databases emphasize flexibility, scalability, and availability.
Choosing between them is not about preference but alignment. The optimal decision depends on how your application manages data, how it scales, and how critical consistency is to your business operations. This understanding leads naturally into evaluating real-world SQL vs NoSQL use cases, which is explored in the next section.
Understanding real-world scenarios is essential when evaluating sql vs nosql. Instead of choosing a database based on popularity, the decision should be guided by how the application handles data, transactions, and scale. This section explains when to use SQL vs NoSQL through common use cases.
SQL databases are best suited for applications where data accuracy and consistency are non-negotiable. Systems that rely on structured records and strong relationships benefit significantly from the relational model.
Use cases such as financial systems, billing platforms, inventory management, and enterprise reporting require strict transactional integrity. In these scenarios, SQL databases ensure that every operation follows consistent rules, making them a reliable choice in many SQL vs NoSQL use cases.
SQL is also well suited for applications that depend heavily on complex queries, aggregations, and multi-table relationships. When reporting and analytics are central to business decision-making, relational databases continue to deliver strong performance.
NoSQL databases are preferred when flexibility and scalability are primary requirements. Applications that generate large volumes of rapidly changing data often struggle within rigid schemas.
Real-time systems such as activity feeds, messaging platforms, IoT applications, and recommendation engines benefit from NoSQL’s ability to ingest and process data at scale. These workloads commonly appear in modern architectures where availability and speed matter more than immediate consistency.
In the broader sql vs nosql discussion, NoSQL becomes the stronger option when applications must scale horizontally across regions and handle unpredictable traffic patterns.
Many modern systems do not rely on a single database model. Instead, organizations often combine both approaches to meet different operational needs.
For example, SQL databases may manage core transactional data, while NoSQL databases handle logs, events, user activity, or session data. This hybrid approach addresses diverse requirements without forcing a single solution across all workloads.
This model reflects a practical answer to the common question of which database to use SQL or NoSQL, especially in large or evolving systems.
The most reliable way to evaluate sql vs nosql use cases is to analyze how the application behaves in production. If the system demands strict consistency, structured data, and relational integrity, SQL is typically the right choice. If the application requires rapid scaling, flexible data models, and real-time responsiveness, NoSQL often provides better alignment.
Understanding usage patterns, growth expectations, and operational complexity is far more valuable than choosing a database based solely on trends.
Share your project idea with us. Together, we’ll transform your vision into an exceptional digital product!

The difference between sql vs nosql lies in how data is stored and managed. SQL databases use structured tables, while NoSQL databases allow flexible data formats, making them suitable for different application needs.
A SQL database is commonly used for applications that require structured data, strong consistency, and reliable transactions such as banking systems, ERP platforms, and order management systems.
A NoSQL database is mainly used for handling large volumes of dynamic or unstructured data, including real-time applications, content platforms, and cloud-based systems.
There is no universal answer in the sql vs nosql debate. SQL works better for structured and transactional data, while NoSQL performs better for scalability and fast-changing workloads.
You should choose SQL when data relationships and accuracy are critical. NoSQL is a better choice when your application needs flexibility, speed, and horizontal scalability.
NoSQL can be faster for high-volume and distributed workloads, while SQL often performs better for complex queries. Speed in sql vs nosql depends on how the database is used.
The best database for web applications depends on the application structure. Many systems use SQL for core data and NoSQL for caching, sessions, and real-time features.
NoSQL databases are generally easier to scale horizontally, which is why they are often chosen for large-scale and cloud-native applications.
Startups often use NoSQL for rapid development and SQL for business-critical data. This combined approach helps balance speed with reliability.
Yes. Many modern architectures use both databases together, selecting the right one based on specific workloads rather than choosing only one.

Have a one on one discussion with our Expert Panel

While companies invest in flutter app development for interactive user interfaces, an app’s performance often becomes the deciding factor in whether users stay or leave. Users may not consciously notice a well‑designed interface, but they immediately feel when an app becomes laggy, slow, or unresponsive.

A major contributor is change detection doing more work than expected. As components grow and templates become more dynamic, Angular evaluates far more bindings per interaction. This pattern sits behind many recurring angular performance issues in large single-page applications.

Most enterprises did not choose to be here. Core systems were built to be stable, not adaptable. Over time, layers of customization, integrations, and workarounds turned reliability into rigidity. Today, every new digital initiative feels harder than it should be.

Founder and CEO

Chief Sales Officer
