
Home » Building Cross-Platform Mobile Apps with React Native: A Beginner’s Guide

In today’s fast-paced digital world, mobile applications have become an essential part of our daily lives. With the increasing demand for mobile apps, developers are constantly looking for efficient ways to create applications that work seamlessly across different platforms. This is where React Native comes into play. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how to build cross-platform mobile apps using React Native, covering everything from the basics to best practices, troubleshooting, and performance optimization.
React Native is an open-source framework developed by Facebook that allows developers to build mobile applications using JavaScript and React. It enables the creation of apps that can run on both iOS and Android platforms, making it a popular choice for cross-platform mobile development. The key advantage of using React Native is that it allows developers to write code once and deploy it on multiple platforms, significantly reducing development time and costs.
Yes, React Native is cross-platform. This means that you can write a single codebase that works on both iOS and Android devices. React Native achieves this by using native components, which allows the app to have a look and feel similar to that of a native app. This is a significant advantage over traditional mobile app development, where separate codebases are required for each platform.
Before diving into improving your mobile app development using React Native, you need to set up your development environment. Here are the steps to get started:
React Native requires Node.js to run. Download and install it from the official website.
Open your terminal and run the following command:
If you plan to develop for Android, download and install Android Studio. Make sure to install the Android SDK and set up an emulator.
Once your environment is set up, create a new project by running:
Now that your environment is ready, let’s create a simple cross-platform mobile application.
Navigate to Your Project Directory:
Run the Application:
Edit the App.js File: Open the App.js file in your favorite code editor and modify it to display a simple message:
Best Practices for Building Mobile Apps with React Native for Beginners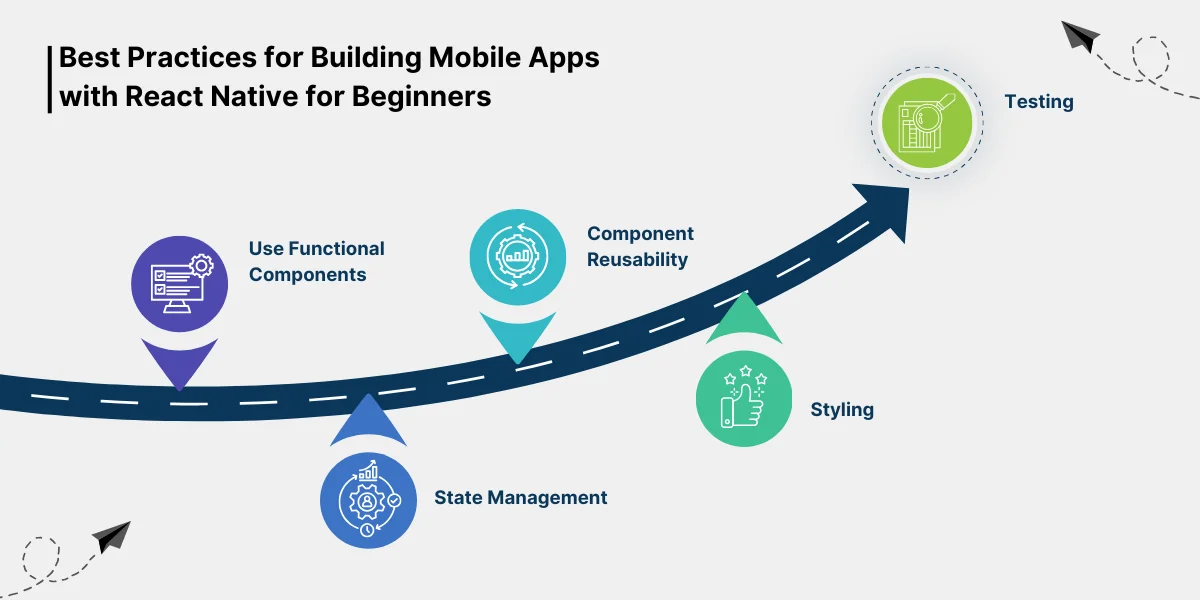
Use Functional Components: Prefer functional components over class components for better performance and readability.
State Management: Use state management libraries like Redux or Context API to manage your app’s state efficiently.
Component Reusability: Create reusable components to avoid code duplication and improve maintainability.
Styling: Use StyleSheet for styling your components. This helps in keeping your styles organized and improves performance.
Testing: Implement testing early in the development process. Use tools like Jest and React Native Testing Library for unit and integration testing.
Get free Consultation and let us know your project idea to turn into an amazing digital product.
Integrating Third-Party Libraries in React Native for Cross-Platform App Development
One of the strengths of React Native is its ability to integrate with a wide range of third-party libraries, which can enhance your app’s functionality and user experience. Here’s how to effectively integrate these libraries:
Choose the Right Library: Before integrating a library, ensure it is well-maintained and compatible with the latest version of React Native. Popular libraries include:
Installation: Use npm or yarn to install the library. For example, to install React Navigation, run:
Usage: Import the library in your component and use it as per the documentation. For instance, to use React Navigation:
Troubleshooting Common Issues When Building Cross-Platform Apps with React Native
While developing with React Native, you may encounter some common issues. Here are solutions to a few of them:
Build Failures: If your app fails to build, ensure that all dependencies are correctly installed and linked. Running npx react-native run-android or npx react-native run-ios again can sometimes resolve the issue.
Hot Reloading Not Working: If hot reloading is not functioning, try restarting the Metro bundler. You can do this by stopping the current process and running:
Performance Issues: If your app is lagging, consider optimizing images, reducing the number of re-renders, and using the should Component Update lifecycle method or React.memo for functional components.
To enhance your react native app development experience, consider using the following tools and resources:
How to Optimize Performance in Cross-Platform Mobile Apps Built with React Native 
Use FlatList for Large Lists: Instead of using ScrollView for rendering large lists, use FlatList, which only renders items that are currently visible on the screen.
Avoid Inline Functions: Inline functions can lead to unnecessary re-renders. Define functions outside of the render method.
Optimize Images: Use appropriate image sizes and formats. Consider using libraries like react-native-fast-image for better performance.
Use Native Modules: For performance-critical tasks, consider writing native modules in Java for Android

User interface design is vital for user engagement. Here are some tips for creating user-friendly interfaces:
Consistent Design: Maintain a consistent design language across your app. Use a design system or component library to ensure uniformity.
Responsive Layouts: Use Flexbox for responsive layouts that adapt to different screen sizes.
Accessibility: Ensure your app is accessible to all users by following accessibility guidelines and using appropriate accessibility props.
User Feedback: Provide visual feedback for user interactions, such as button presses and loading states.
Many successful apps have been built using React Native, showcasing its capabilities. Some notable examples include:

Building cross-platform mobile applications with React Native offers a powerful and efficient way to reach a wider audience while minimizing development time and costs. As we’ve explored in this guide, React Native allows developers to create high-quality apps that run seamlessly on both iOS and Android platforms using a single codebase.
From setting up your development environment to integrating third-party libraries, troubleshooting common issues, and optimizing performance, this guide has provided you with essential knowledge and best practices for mobile app development using React Native.
As you embark on your journey in React for app development, remember to leverage the vast ecosystem of tools and resources available to you. Embrace the community support, explore practical examples, and continuously refine your skills.
By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can create user-friendly interfaces, ensure your app performs optimally, and ultimately deliver a product that meets the needs of your users.
Whether you are a complete beginner or looking to enhance your existing skills, React Native is a valuable framework that can help you succeed in the world of native cross-platform mobile development. So, roll up your sleeves, start coding, and enjoy the process of creating amazing cross-platform applications with React Native.

Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is no longer limited to large, national banks. Smaller financial institutions like community banks, credit unions, and regional institutions have started implementing this modern automation to find real, practical value.
Automation is quickly becoming a major driver of growth in the finance sector. The way it manages rising transaction volumes, complex compliance needs, and other critical processes has caught the attention of many financial institutions.

In this blog, we’ll explore how AI-driven automation is reshaping banking. From boosting operational efficiency to improving compliance and risk management, we’ll look at how this technology is creating smarter, more adaptive financial systems.
React Native allows developers to use a single JavaScript codebase to build apps for both iOS and Android, whereas traditional native development requires separate codebases for each platform, typically using Swift/Objective-C for iOS and Java/Kotlin for Android.
Navigation can be managed using libraries like React Navigation, which provides an easy way to manage routes, tabs, and stacks in your mobile app.
State in React Native is used to store and manage data that can change over time, such as user input, form data, or fetched API data. It allows components to re–render when data changes, ensuring the UI is always up-to-date.
You can handle user input with components like TextInput for text fields and TouchableOpacity for handling touch events. These components capture user interactions and trigger state changes.
You can debug React Native apps using tools like React Native Debugger, Flipper, or by using console.log() statements. These tools help track down errors, inspect the component hierarchy, and analyze network requests.
Handle errors by:
Common challenges include:
You can use libraries by installing them via npm or yarn. After installation, link them to the project if necessary (some libraries require manual linking, though newer versions of React Native handle this automatically).
Hot-reloading allows developers to see changes in the app instantly without the need for a full page reload. This speeds up the development process by reflecting changes in real-time during coding.
For better code organization, follow these practices:
You can create animations using the Animated API or more advanced libraries like React Native Reanimated, which provides a higher-level abstraction for creating complex animations.
To test a React Native app, use testing libraries such as Jest for unit tests and React Native Testing Library for component tests. This ensures that your components and functions behave as expected.
To deploy your app:
For iOS: Use Xcode to build and submit your app to the App Store.
For Android: Generate a signed APK or AAB and upload it to Google Play Console.
Props (short for properties) are used to pass data and functions from parent components to child components. They are immutable and cannot be modified by the receiving component.
You can use libraries like React Native Device Info and Platform API to access device-specific information, such as platform type, version, or hardware specifications.
INDIA : F-190, Phase 8B, Industrial Area, Sector 74,
Mohali, India
CANADA : 55 Village Center Place, Suite 307 Bldg 4287, Mississauga ON L4Z 1V9, Canada
USA :2598 E Sunrise Blvd, Fort Lauderdale,FL 33304,
United States

Founder and CEO

Chief Sales Officer
